24/7 deliverysupport@peptidesceince.com
The best discounts this week
Every week you can find the best discounts here.
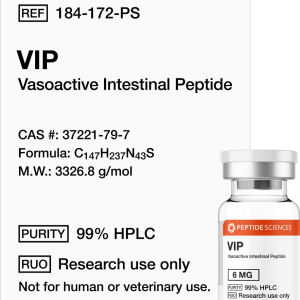
VIP 6mg
Vilon 20mg (Bioregulator)
Vialox (Pentapeptide-3V) 200mg (Topical)
Vesugen 20mg (Bioregulator)
Vesilute 20mg (Bioregulator)
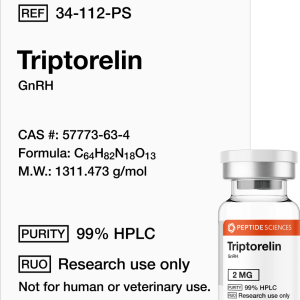
Triptorelin (GnRH) 2mg
Ipamorelin (5mg x 10), CJC-1295 no DAC (5mg x 10)
Humanin 10mg
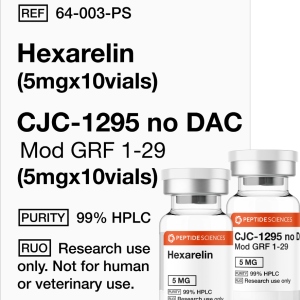
Hexarelin (5mg x 10), CJC-1295 no DAC (5mg x 10)
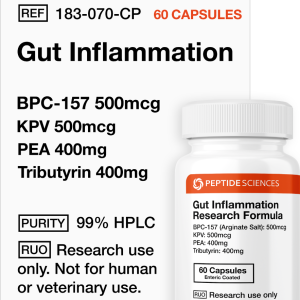
Gut Inflammation (60 Capsules) (Stable BPC-157, KPV, PEA, Tributyrin)
GHK-Cu 200mg (Copper Peptide) (Topical)
Follistatin 315 1mg
Epithalon (Epitalon) 50mg
CJC-1295 (No DAC), Ipamorelin, GHRP-2 (Blend)
CJC-1295 (no DAC), Hexarelin 10mg (Blend)
CJC-1295 (No DAC), GHRP-6 10mg (Blend)
CJC-1295 (No DAC), GHRP-2 10mg (Blend)
BPC-157, TB-500, KPV, GHK-Cu 80mg (Klow Blend)
BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu 60mg (Glow Blend)
- BPC-157: A stable gastric pentadecapeptide shown to accelerate angiogenesis, fibroblast migration, and epithelial repair via modulation of VEGFR2, FAK-paxillin pathways, and nitric oxide signaling. It enhances tendon, muscle, and intestinal healing in preclinical models.
- TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4): A 43-amino acid actin-sequestering peptide that promotes tissue regeneration through cell migration, angiogenesis (via VEGF upregulation), and anti-inflammatory effects. It mobilizes progenitor cells and accelerates repair of myocardium, dermis, and connective tissue.
- GHK-Cu: A copper-binding tripeptide (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) that stimulates wound healing, collagen synthesis, and hair growth. It modulates gene expression linked to tissue remodeling and exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects through TGF-β and metalloproteinase regulation.
- Angiogenesis: TB-500 and BPC-157 both promote VEGF-mediated vascularization, while GHK-Cu enhances endothelial cell proliferation.
- Cellular migration and matrix remodeling: TB-500 improves actin polymerization and cellular motility; GHK-Cu and BPC-157 stimulate ECM production and fibroblast activity.
- Anti-inflammatory modulation: All three reduce oxidative stress and cytokine-driven inflammation, potentially improving healing in chronic or complex injuries.
BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu 30mg (Glow Blend)
- BPC-157: A stable gastric pentadecapeptide shown to accelerate angiogenesis, fibroblast migration, and epithelial repair via modulation of VEGFR2, FAK-paxillin pathways, and nitric oxide signaling. It enhances tendon, muscle, and intestinal healing in preclinical models.
- TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4): A 43-amino acid actin-sequestering peptide that promotes tissue regeneration through cell migration, angiogenesis (via VEGF upregulation), and anti-inflammatory effects. It mobilizes progenitor cells and accelerates repair of myocardium, dermis, and connective tissue.
- GHK-Cu: A copper-binding tripeptide (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) that stimulates wound healing, collagen synthesis, and hair growth. It modulates gene expression linked to tissue remodeling and exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects through TGF-β and metalloproteinase regulation.
- Angiogenesis: TB-500 and BPC-157 both promote VEGF-mediated vascularization, while GHK-Cu enhances endothelial cell proliferation.
- Cellular migration and matrix remodeling: TB-500 improves actin polymerization and cellular motility; GHK-Cu and BPC-157 stimulate ECM production and fibroblast activity.
- Anti-inflammatory modulation: All three reduce oxidative stress and cytokine-driven inflammation, potentially improving healing in chronic or complex injuries.
BPC-157, TB-500 20mg (Blend)
PC-157 and TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) are peptides commonly studied for their potential in promoting tissue repair and healing. Both have distinct yet complementary mechanisms that, when combined, may offer synergistic benefits. BPC-157, a stable gastric pentadecapeptide, is derived from a protective protein found in the stomach lining. It has been shown in preclinical studies to accelerate healing of muscles, tendons, and ligaments by promoting angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) and regulating the production of growth factors. Similarly, TB-500, a fragment of the naturally occurring Thymosin Beta-4 protein, plays a key role in cell migration, tissue regeneration, and reducing inflammation.
The potential synergy between these peptides arises from their overlapping yet distinct pathways in tissue repair. While BPC-157 excels at improving blood flow and reducing inflammation, TB-500 focuses on facilitating cellular migration to the injury site and supporting the repair process at the cellular level. Together, they may accelerate healing by addressing multiple aspects of tissue recovery, particularly in sports injuries or chronic conditions where regeneration is compromised. Early animal studies suggest this combination may lead to faster recovery times and improved structural integrity of repaired tissues.
It is crucial to note that while promising, much of the research on BPC-157 and TB-500 remains preclinical.
BPC-157, TB-500 10mg (Blend)
BPC-157 and TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) are peptides commonly studied for their potential in promoting tissue repair and healing. Both have distinct yet complementary mechanisms that, when combined, may offer synergistic benefits. BPC-157, a stable gastric pentadecapeptide, is derived from a protective protein found in the stomach lining. It has been shown in preclinical studies to accelerate healing of muscles, tendons, and ligaments by promoting angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) and regulating the production of growth factors. Similarly, TB-500, a fragment of the naturally occurring Thymosin Beta-4 protein, plays a key role in cell migration, tissue regeneration, and reducing inflammation.
The potential synergy between these peptides arises from their overlapping yet distinct pathways in tissue repair. While BPC-157 excels at improving blood flow and reducing inflammation, TB-500 focuses on facilitating cellular migration to the injury site and supporting the repair process at the cellular level. Together, they may accelerate healing by addressing multiple aspects of tissue recovery, particularly in sports injuries or chronic conditions where regeneration is compromised. Early animal studies suggest this combination may lead to faster recovery times and improved structural integrity of repaired tissues.
It is crucial to note that while promising, much of the research on BPC-157 and TB-500 remains preclinical.