BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu 60mg (Glow Blend)
Mechanisms and Synergy
- BPC-157: A stable gastric pentadecapeptide shown to accelerate angiogenesis, fibroblast migration, and epithelial repair via modulation of VEGFR2, FAK-paxillin pathways, and nitric oxide signaling. It enhances tendon, muscle, and intestinal healing in preclinical models.
- TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4): A 43-amino acid actin-sequestering peptide that promotes tissue regeneration through cell migration, angiogenesis (via VEGF upregulation), and anti-inflammatory effects. It mobilizes progenitor cells and accelerates repair of myocardium, dermis, and connective tissue.
- GHK-Cu: A copper-binding tripeptide (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) that stimulates wound healing, collagen synthesis, and hair growth. It modulates gene expression linked to tissue remodeling and exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects through TGF-β and metalloproteinase regulation.
Synergistic Benefits:
Combined research with BPC-157, TB-500, and GHK-Cu may offer synergistic tissue regeneration and anti-inflammatory benefits by concurrently activating multiple repair pathways:
- Angiogenesis: TB-500 and BPC-157 both promote VEGF-mediated vascularization, while GHK-Cu enhances endothelial cell proliferation.
- Cellular migration and matrix remodeling: TB-500 improves actin polymerization and cellular motility; GHK-Cu and BPC-157 stimulate ECM production and fibroblast activity.
- Anti-inflammatory modulation: All three reduce oxidative stress and cytokine-driven inflammation, potentially improving healing in chronic or complex injuries.
This multifactorial synergy suggests enhanced efficacy in musculoskeletal, dermatological, and post-surgical recovery applications.
- 24/7 Delivered
- Including shipping costs.
- 30 day money refund
- Day and night customer service
Description
BPC-157 + TB500 (Thymosin Beta 4) + GHK-Cu Blend
BPC-157, TB500, and GHK-Cu are, separately, some of the most potent anti-inflammatory peptides that have been investigated. Each of these peptides has been found to promote wound healing, slow tissue decay, promote muscle and tendon growth, alter DNA expression patterns, and even thwart the effects of aging. Despite their similar properties, however, each of these peptides works in a different way to bring about its various effects. Thus, logic would dictate that using these peptides in conjunction with one another could result in synergies in each of the areas mentioned above.
To aid in research into the combined effects of these peptides, a BPC-157 + TB500 (Thymosin Beta 4) + GHK-Cu Blend has been created. This blend makes ordering, storage, dosing, and administration of these peptides easier, allowing researchers to focus on measuring outcomes and designing experiments rather than creating protocols for administering multiple individual peptides.
What follows is a look at how BPC-157, TB500, and GHK-Cu might work in conjunction and why they might produce synergistic (i.e. enhanced effects) when used in combination. This overview will likely provide some guidance on what animal studies using these peptides in combination might uncover and where scientists should expect to see results.
BPC-157: Biochemistry
BPC-157 is a penta-decapeptide derived from the naturally occurring Body Protective Compound (BPC). BPC was originally derived from human gastric contents and has been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. Animal studies have indicated benefit in the GI tract, liver, pancreas, ligaments, muscles, tendons, cornea, heart, brain, and nerves.
The precise way in which BPC-157 produces its effects is still not clearly understood. For instance, it isn’t clear if the peptide binds to a cell surface receptor to produce its effects or if it is transported into the cell and perhaps has effects directly at the level of the DNA. A few things about BPC-157 have become clear from the research, however. First, BPC-157 has profound effects on nitric oxide (NO) signaling. Many of its properties are thought to relate, in some way, to the ability of BPC-157 to influence NO signaling at the levels of eNOS expression.
Second, BPC-157 is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Research shows that 10 minutes after administration, BPC-157 can be found relatively evenly spread throughout the body including kidney, liver, stomach wall, thymus, gonads, and spleen. Peak levels of the peptide are achieved in tissue approximately 1 hour after administration and then slowly decline over the next 48 hours [1]. Levels tend to me highest in kidney, liver, thymus, and spleen with slightly lower levels in lung, muscle, brain, and skin.
The third thing that can be concluded about the biochemistry of BPC-157 is that it alters gene expression patterns. Again, the mechanism by which this occurs has yet to be elucidated, but the peptide definitely alters expression patterns of:
• Egr,
• Nos (especially eNos),
• Srf,
• Vegr,
• Plcγ, and
• Kras.
These genes control the synthesis of a number of factors that affect cells of blood vessels and the immune system such as adhesion, thrombosis, and inflammatory responses. The levels of each gene increased or decreased based on the timeframe following administration of BPC-157. This suggests that BPC-157 is working through a regulatory mechanism that has fine-grained control over a wide array of genes and their expression.
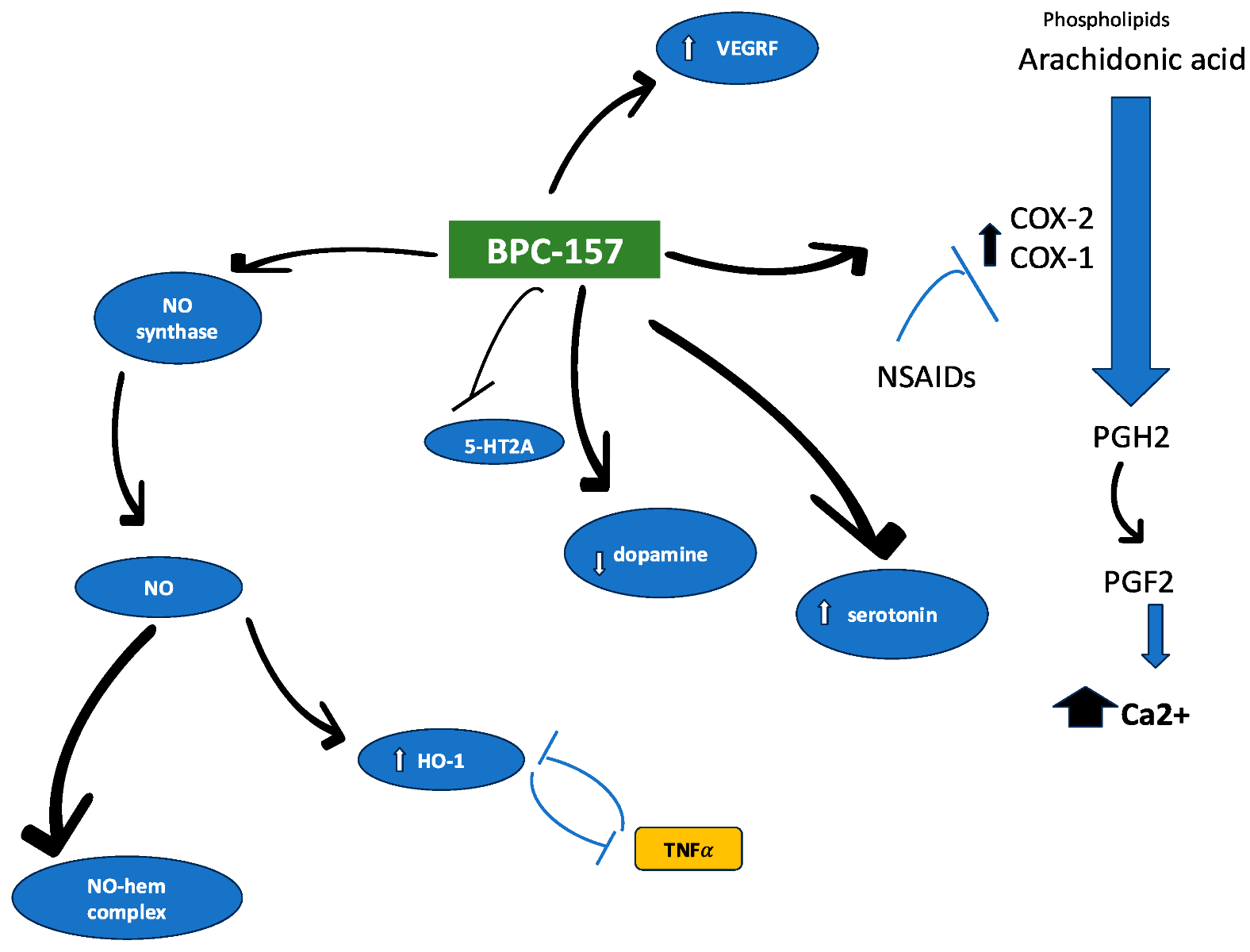
An Overview of the complex actions of BPC-157 in the body. Note the profound effects on NO signaling and VEGF expression as well as several impacts on inflammatory cytokines.
Source: MDPI
It is important to return to the fact that one of the major actions of BPC-157 (if not THE major action) is in nitric oxide (NO) signaling. Research shows that BPC counteracts the deleterious effects of L-NAME, which has been known to cause ulceration in the GI tract. Additionally, BPC-157 has been shown to positively influence nitric oxide synthase (NOS and especially eNOS), leading to increased expression of several antioxidant enzymes, such as heme oxygenase (HO-1). At the same time, nitric oxide (NO) produced by NOS plays a dual role. While it can exhibit cytotoxic effects, it also contributes to immune responses and is essential for the functioning and development of neurons. NO can directly bind to the heme group in NOS, initiating a variety of chemical and biochemical processes. These include NO deoxygenation, which is linked to its scavenging and vasoconstrictive effects—particularly relevant in conditions like hemolytic disorders—as well as the S-nitrosylation of hemoglobin, a process implicated in lung injury and associated with elevated red blood cell production[2].
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.